The Care Home Improvement Programme (CHIP) – Cohort 1, led by the Care Inspectorate, aimed to support care home staff to apply quality improvement to improve outcomes for people experiencing care. The full case study and summary are available below.
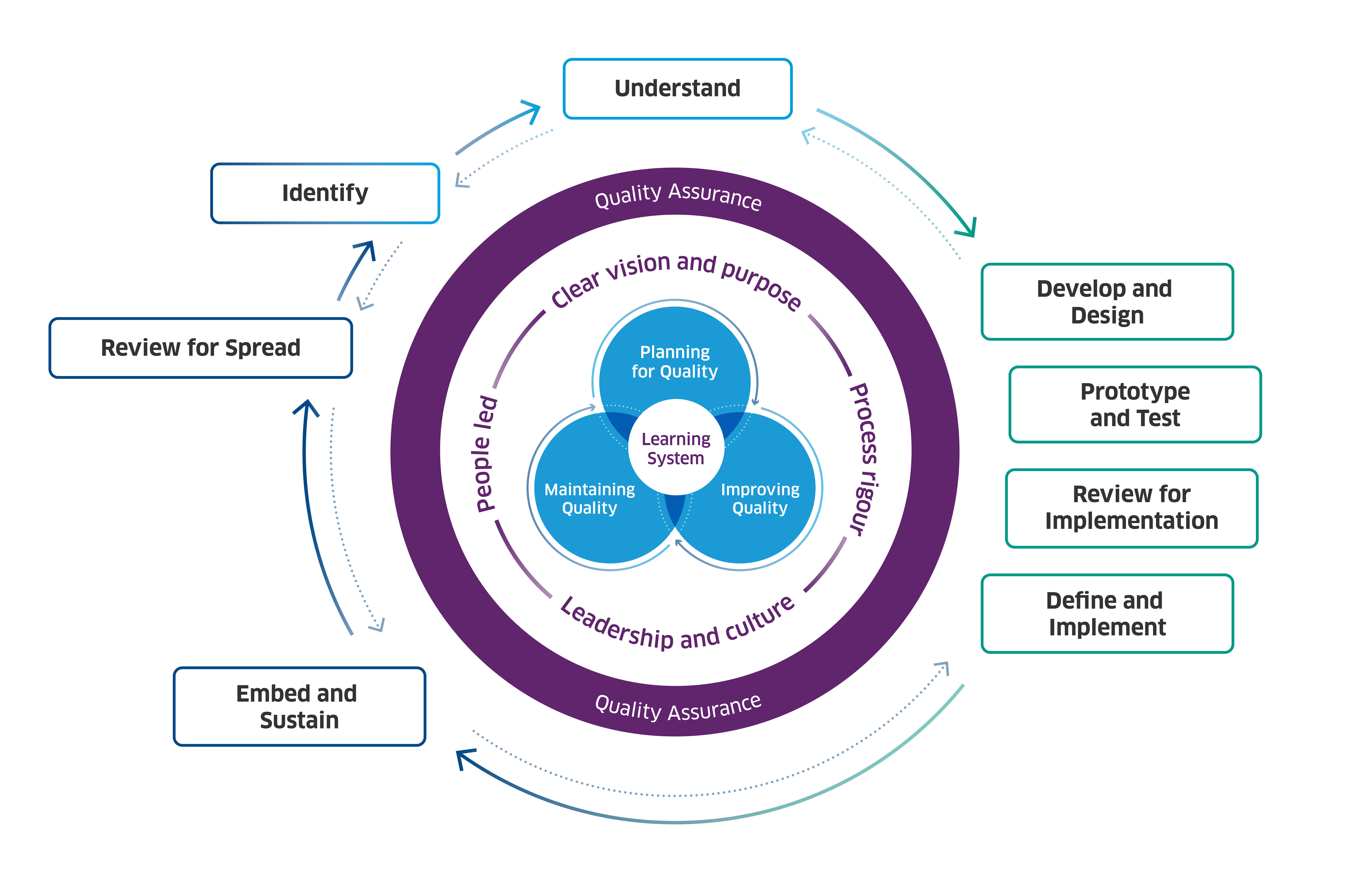
Steps of change
Identify
Identified the problem: care homes with an “adequate” inspection rating were not consistently applying quality improvement methods, which limited their ability to improve outcomes for residents. There was a need to build capability and confidence in quality improvement.
Understand
Completed evidence review and needs assessment which identified that targeted support could help care homes better understand and apply improvement approaches.
Develop and design
The programme was structured around themes – self-evaluation, quality improvement, leadership, and celebration. Improvement Advisors provide tailored support to care homes. Care homes selected improvement topics based on their inspection reports.
Prototype and test
Each care home undertook an improvement project using quality improvement methods. Topics included mealtime experience, meaningful activity, and documentation. Improvement Advisors supported testing through individual and group sessions.
Review for implementation
Evaluation data showed that learning would improve care, increased knowledge of quality improvement, and increased confidence applying improvement methods. Positive relationships with the Care Inspectorate also increased.
Define and implement
There was an iterative implementation process. Care homes were supported to embed learning and apply it in practice. Leadership development was supported by the Scottish Social Services Council.
Embed and sustain
Peer support and local networking were key enablers for sustainability. Participants reported increased confidence, improved relationships with regulators, and enhanced resident wellbeing. The programme helped embed a culture of improvement.
Review for spread
Participant feedback strongly endorsed the programme. The structure and support model provide a replicable framework for future cohorts. The success of Cohort 1 lays the groundwork for broader rollout across Scotland.
Enablers of quality and change
Clear vision and purpose
A clear vision helped to provide direction, motivation, and alignment, including:
- a shared goal to improve care through quality improvement
- alignment with Care Inspectorate’s strategic priorities
- focus on practical, resident-centred improvements
Leadership and culture
Leadership and culture were critical in driving the change forward, including:
- embedding of leadership development in the programme
- fostering a culture of collaboration and openness through peer support
- building trust and engagement through strong improvement advisor relationships
People-led
Ensuring a people led approach to change was essential, including:
- improvement topics were chosen by care homes based on inspection feedback
- staff led improvement projects to ensure relevance and ownership
- peer learning and shared experiences enhanced engagement
Process rigour
Ensuring process rigour was key to ensuring high-quality and reliable outcomes, including:
- a structured programme with defined stages and support
- use of improvement methodology ensured consistency
- evaluation and feedback mechanisms tracked progress and impact
